A team led by Prof. LI Can designed a new solar-driven electrochemical process that could realize the simultaneous conversion of CO2 and H2S into value-added products. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
CO2 and H2S are generally concomitant with methane in natural gas and traditionally deemed useless or even harmful. Therefore, it's needed to pretreat these gases for further processing. If CO2 and H2S can be used to produce value-added products, more economic and environmental benefits will be obtained.
Previous research are mainly focused on H2S conversion. For example, H2S was converted into sulfur and water in air with Claus technology. So far, there are rare reports on the simultaneous conversion of CO2 and H2S into value-added chemicals.
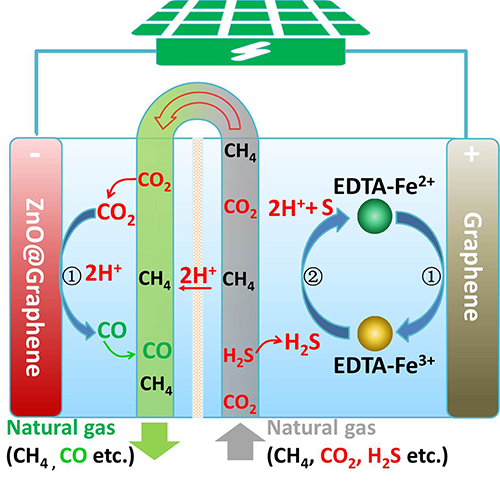
Illustration of coupled electrochemical transformation of CO2 and H2S on non-precious metal catalysts. (Image by MA Weiguang)
"Our as-prepared solar-driven electrochemical system can realize the simultaneous conversion of CO2 and H2S into carbon monoxide and sulfur at an atom-economical way." said Prof. LI.
They developed a novel solar-driven electrochemical process which was demonstrated using zinc oxide encapsulated by graphene catalyst for CO2 reduction and graphene catalyst for H2S oxidation mediated by EDTA-Fe2+/EDTA-Fe3+redox couples. This conceptually provided an alternative avenue for the purification of natural gas with added economic and environmental benefits.
Aiming to solve the energy and environmental issues, Prof. LI's team has been dedicating to converting CO2 and H2S to useful chemicals with renewable energy resources.
As for CO2, they designed ZnO-ZrO based catalysts for selectively conversion of CO2 to methanol and lower olefins, respectively (Sci Adv., ACS Catal.).
Moreover, several approaches such as photocatalytic, photoelectrochemical and photovoltaic-electrochemical strategies have been developed to convert H2S into value-added chemicals (J. Catal., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Energy Environ. Sci., ACS Catal.). It is worth noting that high quantum efficiency of up to 93% was obtained for photocatalytic H2 production from H2S splitting reaction under visible light irradiation, which represents a benchmark value in this field.
The new finding of producing value-added chemicals by consuming CO2 and H2S simultaneously provides an environmentally benign and economically feasible avenue for the purification of natural gas.
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China and National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Texted by MA Weiguang)